OpenAPI Authentication in Nexios
Securing your API is essential for protecting user data and enabling safe integrations. Nexios supports multiple authentication schemes and provides first-class OpenAPI documentation for each.
1. Why Secure Your API?
APIs without authentication are vulnerable to abuse and data leaks. Always protect sensitive endpoints!
Example:
python
@app.get("/public")
async def public_info(req, res):
return {"info": "Anyone can see this."}
@app.get("/private", security=[{"bearerAuth": []}])
async def private_info(req, res):
return {"info": "Only authenticated users see this."}2. Bearer (JWT) Authentication
JWT (JSON Web Token) is the default method. Nexios includes a bearerAuth scheme automatically.
How to Require JWT Auth
python
from nexios import NexiosApp
app = NexiosApp()
@app.get("/profile", security=[{"bearerAuth": []}], summary="Get user profile (JWT required)")
async def get_profile(req, res):
# req.user is set after authentication
...What does this look like in docs?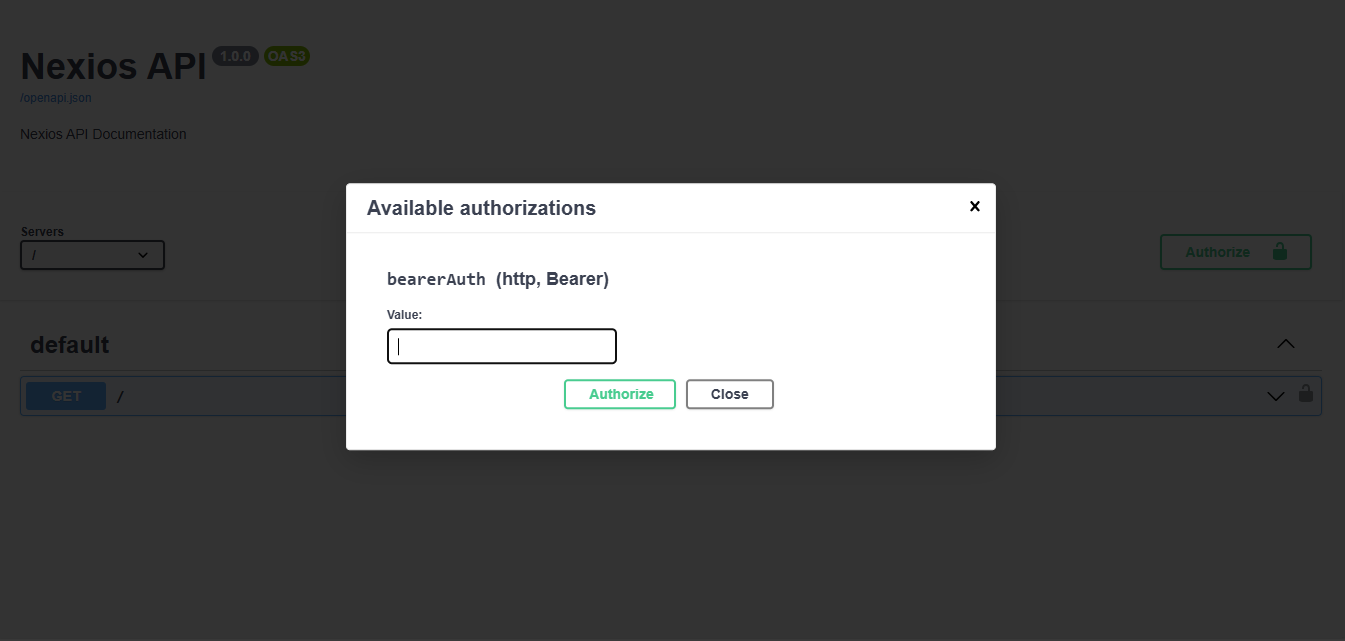
Multiple JWT-Protected Endpoints
python
@app.get("/settings", security=[{"bearerAuth": []}])
async def settings(req, res): ...
@app.post("/posts", security=[{"bearerAuth": []}])
async def create_post(req, res): ...Customizing Bearer Scheme
python
from nexios.openapi.models import HTTPBearer
app.docs.add_security_scheme(
"jwtAuth",
HTTPBearer(
type="http",
scheme="bearer",
bearerFormat="JWT",
description="JWT token required in Authorization header"
)
)3. API Key Authentication (Header, Query, Cookie)
API keys are great for simple, programmatic access. You must register the scheme first.
Register an API Key Scheme
python
from nexios.openapi.models import APIKey
app.docs.add_security_scheme(
"apiKeyAuth",
APIKey(
name="X-API-KEY",
**{"in": "header", "description": "Your API access key", "type": "apiKey"}
)
)Require API Key on an Endpoint
python
@app.get("/admin", security=[{"apiKeyAuth": []}], summary="Admin access (API Key)")
async def admin_panel(req, res):
...Use API Key in Query or Cookie
python
APIKey(
name="api_key",
**{"in": "query", "description": "API key as query parameter", "type": "apiKey"}
)
APIKey(
name="session_id",
**{"in": "cookie", "description": "Session cookie", "type": "apiKey"}
)4. OAuth2 Authentication (with Scopes)
OAuth2 is for delegated, third-party access. Nexios supports all flows.
Register OAuth2 Password Flow
python
from nexios.openapi.models import OAuth2, OAuthFlows, OAuthFlowPassword
app.docs.add_security_scheme(
"oauth2",
OAuth2(
flows=OAuthFlows(
password=OAuthFlowPassword(
tokenUrl="/auth/token",
scopes={
"read": "Read access",
"write": "Write access",
"admin": "Admin privileges"
}
)
),
description="OAuth2 password flow authentication"
)
)Require OAuth2 with Scopes
python
@app.get("/admin", security=[{"oauth2": ["admin"]}], summary="Admin-only endpoint")
async def admin_dashboard(req, res):
...5. Combining Security Schemes
You can require multiple or alternative auth methods.
Example: JWT or API Key
python
@app.get("/superuser", security=[{"bearerAuth": []}, {"apiKeyAuth": []}])
async def superuser_panel(req, res):
...6. Best Practices & Troubleshooting
- Register all security schemes before referencing them.
- Use clear, descriptive names for each scheme.
- Document which endpoints require which auth.
- For public APIs, prefer OAuth2 for flexibility.
- Test your docs UI to ensure all auth flows work as expected.
See also:
